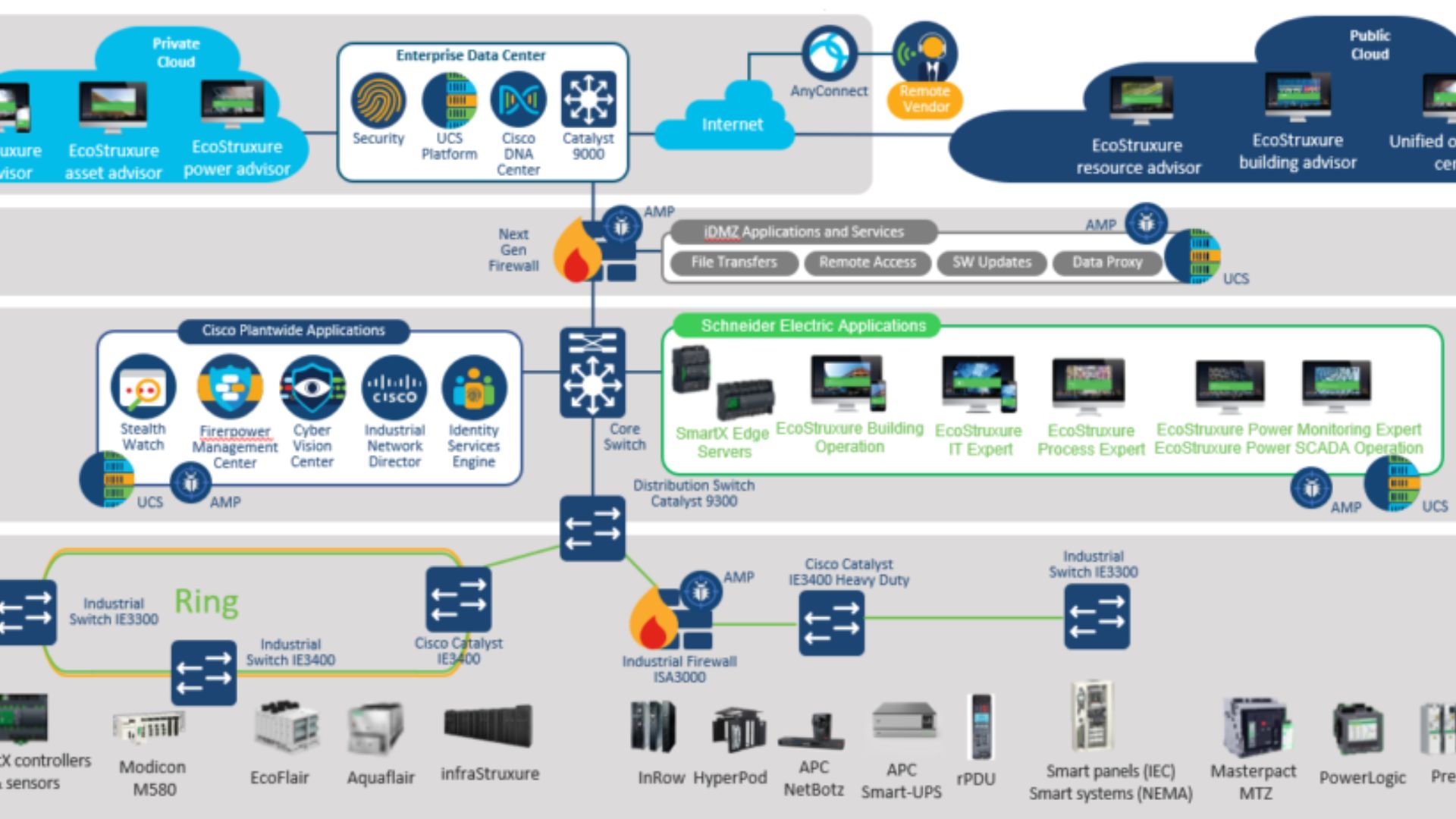
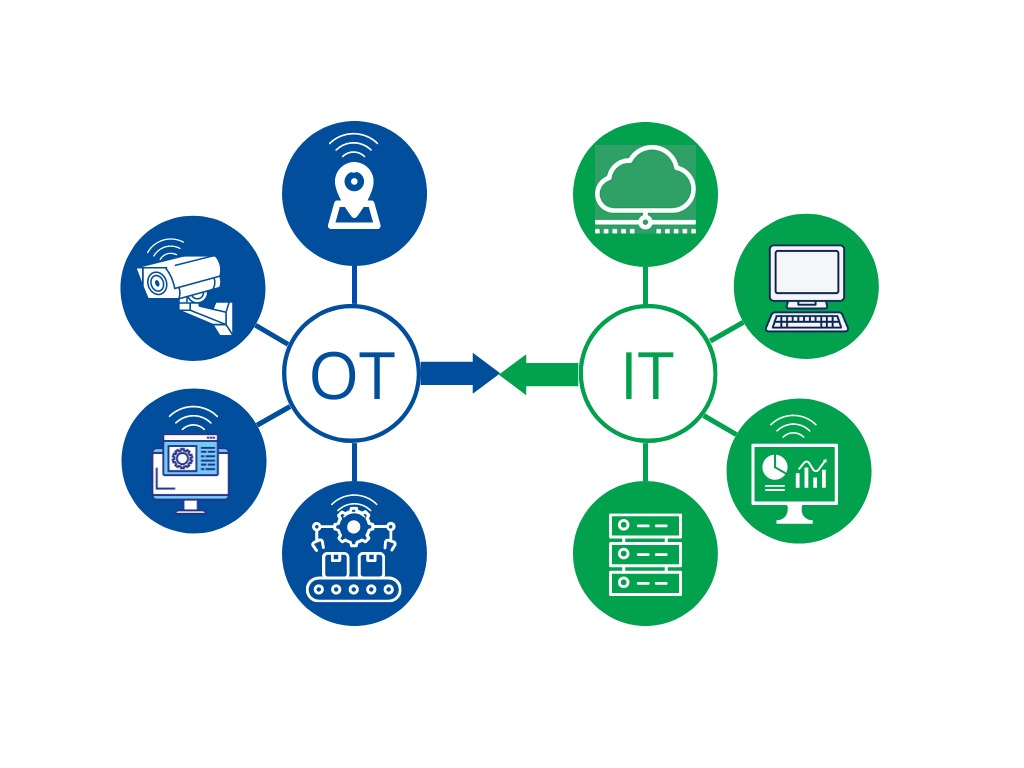
When operational technology (OT) meets the digital world, it's more important than ever to find and keep an eye on all threats. The blog goes into great detail about how to protect essential systems in Operational Technology, showing how hard it is to deal with cyber threats.
It directly answers the question, "How do IT/OT network owners monitor this area for potentially malicious behavior?" by looking at how hard it is to keep OT systems safe from unauthorized access, strange resource use, and changes to the configuration.
As businesses struggle with the merging of real and digital worlds, it becomes clear that they need to be extra careful about finding and responding to threats in OT. This introduction sets the stage for a deep look at the best practices and tools that IT/OT network owners need to protect their networks from cyber dangers in the ever-changing world of operational technology.
What Is Threat Detection, Investigation, And Response?
As used in OT, Threat Detection, Investigation, and Response (TDIR) is the process of finding, evaluating, and reducing cyber threats and incidents in vital infrastructure and industrial control systems (ICS).
OT environments, like those in manufacturing, energy, and utilities, have their problems and needs that are different from those in regular IT systems. To give you an idea of what TDIR means in OT, here are some examples:
Threat Detection In OT
- Network anomaly detection- It is the ongoing checking of network data for strange patterns or actions that could point to a cyber threat. A sudden rise in data flow to a particular programmable logic controller (PLC), for instance, could be a sign of an attempted intrusion.
- Asset inventory and vulnerability scanning- This involves keeping track of all OT assets (like sensors, PLCs, and HMIs) and doing vulnerability checks to find weak spots. For example, scanning ICS devices for unpatched vulnerabilities is one way to do this.
Investigation In OT
- Incident response playbooks- Here, one makes incident reaction plans that are specifically made for OT environments. These playbooks spell out who is responsible for what and what needs to be done during a security event, like when an industrial controller is thought to have malware on it.
- Forensic analysis - Forensic investigations are used to find out what happened and how bad it was. For example, log files from a SCADA system are looked at to find out where a power grid interruption came from.
Response In OT
- Isolation and segmentation - By using this method, you can quickly separate hacked devices or parts of the OT network from the rest of the network to stop the spread of malware or unauthorized access. For example, in a manufacturing plant, you could separate a hacked sensor network.
- Backup and recovery - After something terrible happens, like ransomware attacking a power company's control systems, a robust backup and recovery plan is in place to get OT systems back to a known good state.
- Patch management- As a reaction, security patches and updates are applied to vulnerable OT components while making sure that critical operations are interrupted as little as possible. For example, the firmware of SCADA controllers is updated to fix known vulnerabilities.
- Incident reporting - In this process, incidents are reported to the right people, like government agencies in charge of protecting critical infrastructure, to make sure they are in line with regulations.
The ICS Cybersecurity Considerations Checklist
You can better protect your critical infrastructure from threats with the help of a cybersecurity system that can better and automatically find all of your ICS assets and manage them while using robust defense strategies.
But how do you figure out which OT option will work best for your business? As you work to protect and manage your critical infrastructure, will the options you're looking at help both your OT engineers and your IT security teams?
This ICS cybersecurity checklist was made to help you look at six critical areas to make sure you're picking the best option for your business.
- Automated control and discovery of assets
- Finding and responding to incidents
- Monitoring network traffic all the time
- Validation of controller integrity
- Evaluation of vulnerabilities and control of risks
- Architecture and getting the business ready
Tools For OT Cybersecurity Monitoring
Some tools and solutions can help businesses successfully keep an eye on and respond to OT cybersecurity incidents. When it comes to making OT cyber security solutions safer, these tools are essential. Here are some essential tools:
SIEM Tools
SIEM tools are made to gather and look through logs from many different systems, including OT systems, to find odd behavior and security problems.
Network Monitoring Tools
These tools keep an eye on network traffic to find strange behavior or other actions that could be harmful. They give you real-time information about network security.
Asset Management Tools
Asset management tools help businesses keep track of and organize their OT assets, such as hardware, software, and firmware. This makes it easier to find security holes.
Vulnerability Management Tools
Vulnerability management tools find and rate OT systems' security holes so that patches and other fixes can be made quickly.
SOAR Tools
Security Orchestration, Automation, and Response (SOAR) tools make security jobs like incident response more efficient and quick by automating them.
What Is Essential To Look For In An OT Cyber Security Monitoring Tool?
When looking at an OT cyber security tracking tool, the following things should be true:
Works Without Interfering With Your OT System Function
If your OT security tracking tool stops your system from working and data from moving, the security benefits might not be worth the operational costs. The best OT cybersecurity tool will be able to analyze data without getting in the way.
This is usually done by making and working with a mirrored network traffic stream instead of the actual data stream. It's also essential to do this so that the technology used for tracking can't be used to attack your OT systems.
Automated Learning Of Your System Norms And Baselines
Setting the limits for your OT monitoring tool by hand takes a lot of time and effort. Also, setting policies by hand in an industrial ecosystem that is constantly changing can lead to information that needs to be updated, which can cause your OT tracking tools to give you both false negatives and false positives.
A good OT network tracking tool will have machine-learning features that can create both a baseline topology and a historical trend baseline for system activity. There should always be an opportunity to review and make changes by hand, but it should go along with the automated learning and conclusions.
Detects Both Vulnerabilities And Threats
In the world of cyber security (or any security), a little bit of protection is worth a lot of having to fix things after an attack.
A complete OT cyber security monitoring system will find both attack vectors that can affect your systems, like misconfigured devices or networks or holes in access and trust, as well as threats that are already happening, like strange network traffic, resource use, or changes to configurations.
Passive Monitoring Step-By-Step
Do you use an old version of Windows in your plant, like Windows XP? Is it not possible to patch or upgrade your operating system because of things that affect output, like legacy systems, old hardware, or the need for high uptime? In these situations, you should make up for it by constantly watching to find breaches quickly.
Automatic Asset Identification
ProjectBinder will find new assets instantly and add them to our threat monitoring. Because of this, your staff won't have to do any routine work, and you'll always have an up-to-date list of OT assets.
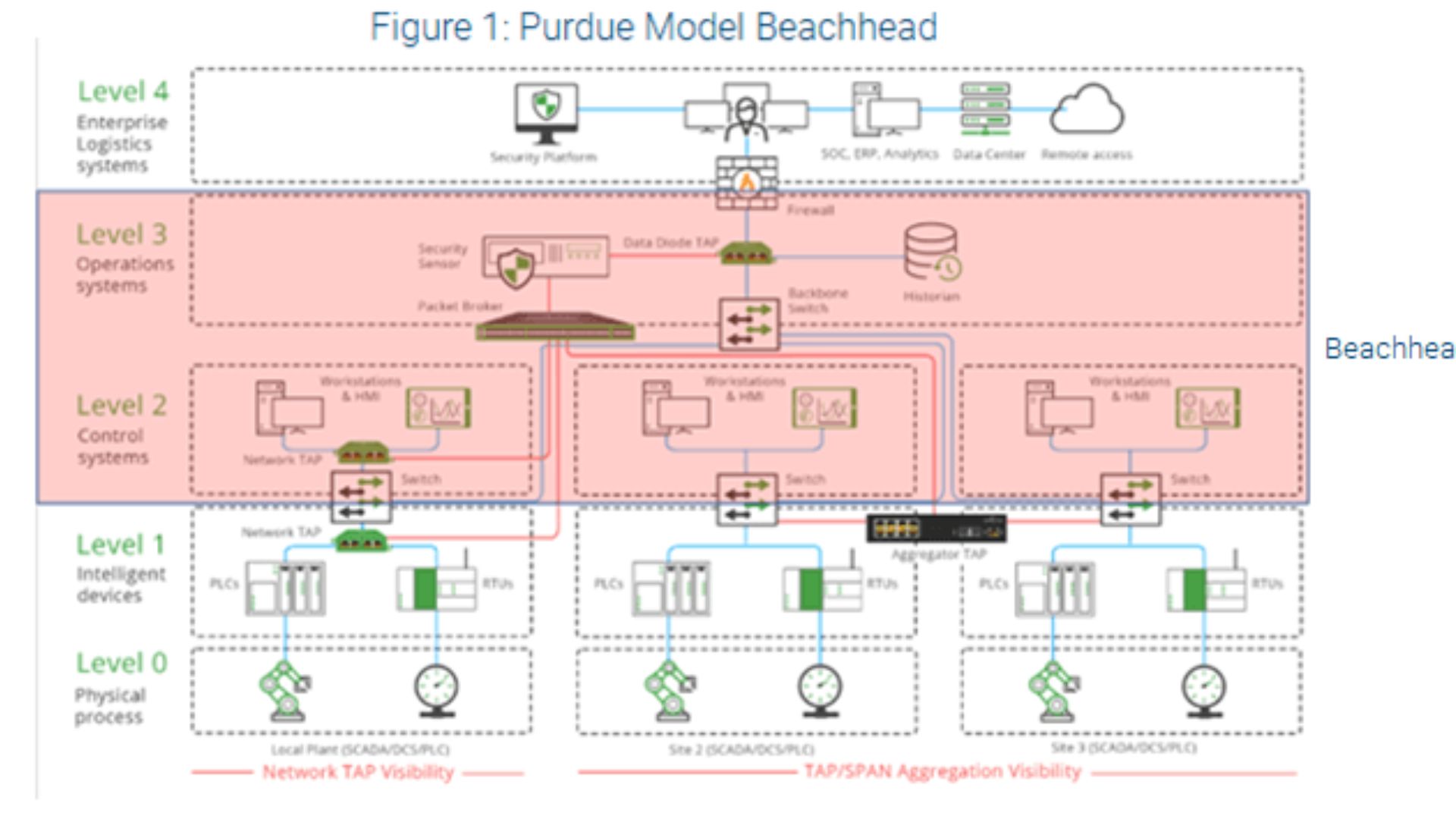
Virtual Purdue Zoning
Virtual Purdue Zoning set up virtual areas on your network that match the Purdue Framework. As an option to physically divide networks, these virtual zones work just as well and cost less. With virtual segmentation, we can separate information between layers, and devices can even be separated within network layers.
Malware Communication
Malware communication checks our network data for known malware and also looks for strange behavior from users and devices.
Contextual Baseline
By keeping an eye on the assets and interactions in your OT network, you can set a standard for how things should generally work in those networks.
Automatic Alerting Into SIEM
SIEM lets you know through your SIEM system so that your security operation center can handle alerts in a way that makes sense with the platform you already have.
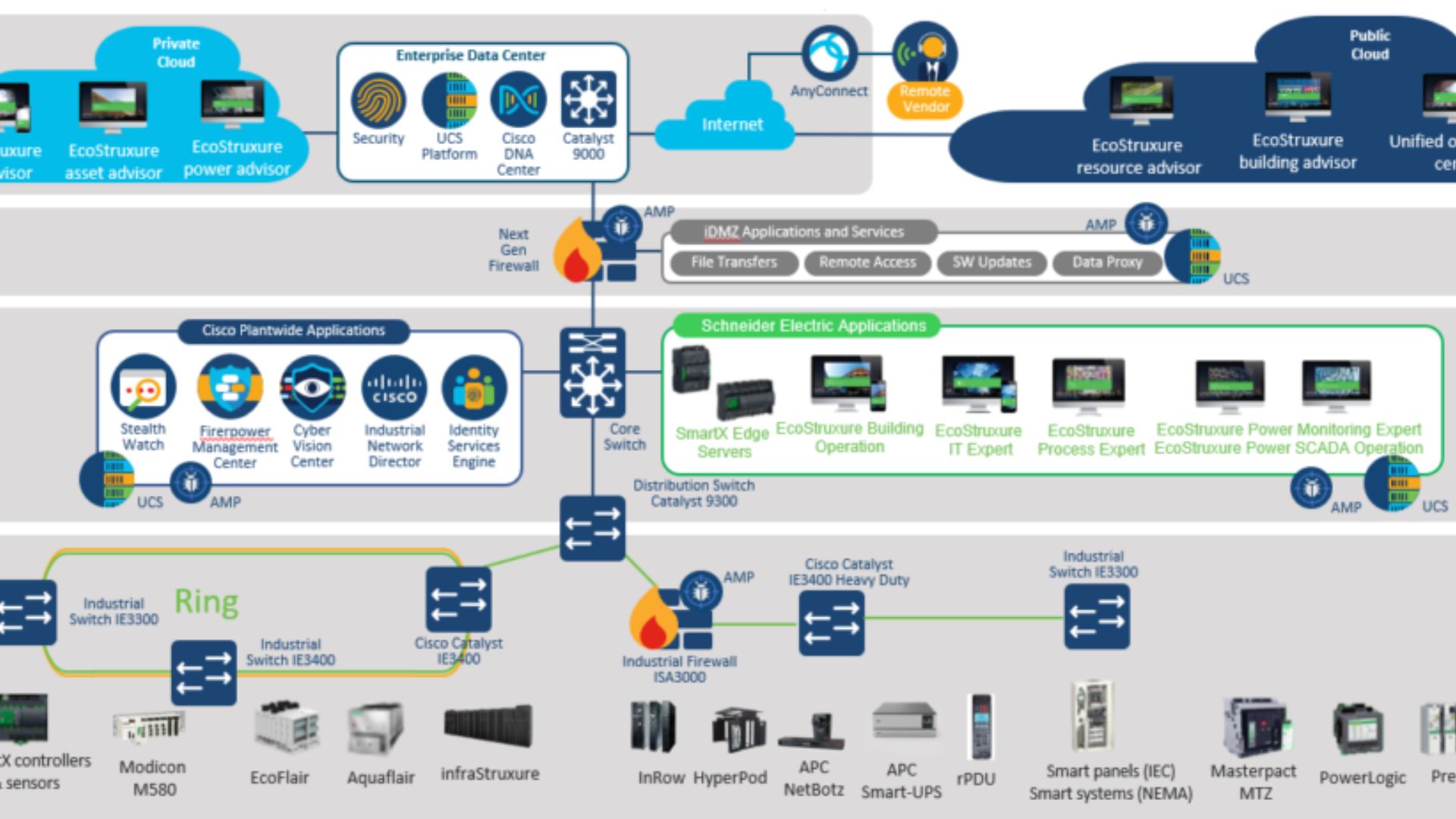
IT/OT Network Segmentation Best Practices
The proper IT-OT network separation methods also have several other advantages, such as:
- It is easier to find and stop cyberattacks when networks are segmented. The OT network is a closed system, so there shouldn't be much contact between it and the IT network. If there is communication that doesn't make sense, it can be reported and looked into. In addition, network separation makes it easier to separate the attacked areas of the network, which lowers the damage that could be done.
- Network segmentation dramatically improves the management and awareness of the network. It also makes things easier to maintain and keep track of by making it clear who is responsible for what when multiple teams are involved.
- Different security methods can be used for each network because of segmentation. For instance, the OT network might need a higher level of physical security (like biometrics) to keep people from getting in without permission. In contrast, the IT side might only need more robust defenses and antivirus software.
- Access rules can be set up for each network thanks to segmentation. Different people, like administrators, managers, and regular employees, may need different amounts of access to the IT network. In the same way, different roles, like operators and maintenance staff, may need different amounts of access to the OT network. By dividing networks into segments, access rules can be put in place to stop people from getting into certain parts of the network without permission.
- Using zone (a business unit or a collection of similar business units, as defined in the IEC 62443 standard) and boundary segmentation, the OT network's traffic flow is further limited. This makes it easier to spot any changes, mistakes, or insider threats made by network administrators that aren't supposed to happen, as well as any new or suspicious traffic.
- There are many times when the process of network division finds unknown or unused devices that would not have been found otherwise.
Frequently Asked Questions
How Do You Monitor An OT System?
Employ continuous monitoring using intrusion detection systems to detect and respond to anomalies in real-time.
What Are The Security Measures For OT?
Implement strict access controls, conduct regular security audits, and ensure firmware/software updates are timely and secure.
What Is Network Segmentation In OT Security?
Divide the OT network into isolated segments to contain and mitigate the impact of security incidents, preventing lateral movement of threats.
What Are The Security Issues With OT?
Vulnerabilities include lack of patch management, insecure remote access, and insufficient encryption, posing risks of unauthorized access and operational disruption.
Conclusion
OT critical infrastructure protection needs comprehensive Threat Detection, Investigation, and Response. Effective monitoring uses SIEM, network monitoring, asset management, and vulnerability assessment to detect abnormalities and threats.
Automation, incident response, network monitoring, and controller integrity certification are the checklist's highlights. The key is choosing an OT cybersecurity monitoring platform that works effortlessly without affecting OT functions, uses automated learning for system norms, detects vulnerabilities and active threats, and provides passive monitoring.
IT/OT network segmentation improves cyberattack detection, network management, security, and role-based access controls. In the ever-changing world of OT security, how do IT/OT network owners monitor this area for potentially malicious behavior? is answered by modern technologies, vigilant techniques, and proactive threat prevention.